Environmental Factor of Ecology
Dosen
pengampu:
1.
Dr. Hadi
Suwono, M.Si
2.
Dr. Vivi
Novianti, S.Si, M.Si.
Ecological
Factors that Constitute the Environment of an Organism
In any eco-system, a living organism is influenced by a
number of factors and forces. These environmental factors are known as eco-
factors or ecological factors. These factors may be biotic (living) and abiotic
(nonliving).
A. ABIOTIC
I. Climatic or Aerial factors:
(a)
Light
Light plays an important role in the species
composition and development of vegetation. And,
on an average approximately only 2-3% of this solar energy is used in Primary Productivity.
Light intensity shows special variations due to the factors like atmospheric
water layer, particles dispersed in the air, etc.
v Effect of
Light on Plants:
1.
The synthesis of chlorophyll in green
plants can take place only in the presence of light.
2. The rate of
photosynthesis is slower at lower intensity
3. Respiration
increases at higher light intensity and it decreases at lower light intensity.
4. The process
of opening of stomata (which depends upon light) leading to loss of water from
the aerial surface of plants is known as transpiration.
5. Light
inhibits the synthesis of auxins or growth hormones
6. The
intensity of light largely influences the growth and development of flowers,
fruits and vegetative parts of plants.
7. Intense
light helps in the formation of anthocyanin pigments in plants.
8. Effect on Movement phototropism The leaves grow transversely to
light.
9. Effect on Photoperiodism The response of plants to the relative
length of the day. classified into Long
Day Plants, Short Day Plants, Day neutral Plants
10. The
germination of seeds is largely influenced by light.
11.
The duration and intensity of light plays an
important role in determining the distribution of plants.
v Effect of
Light on Animals:
1. The rate of
metabolism in animals is largely influenced by light intensity through enzyme
activity.
2. the
breeding activities are induced by light through its inoculating action over
the gonads.
3. Light
induces the formation of pigments in animals.
(b)
Temperature
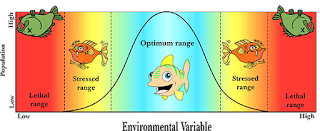
The cardinal temperature (The minimum, optimum and maximum
temperatures) varies from species to species, and in the same individual from
part to part. The distributions of plants, animals are also influenced by temperature.
v Effects of Temperature on
Plants and Animals:
1. In the extremely low
temperature, the protoplasm may be frozen. On the other hand, in the extremely
high temperature, the protein may coagulate or denaturation.
2. Respiration increase when
temperature increase.
3. The growth and development
of plants and poikilothermic animals is influenced by temperature.
4. The transpiration increases
with increase in atmospheric temperature
(c)
Water
The most important for life. All physiological process take
place in the medium of water.
·
Depending on requirement of
water, plants groped into:
1.
Hydrophytes: Plants living in water require large quantities
of water.
2.
Xerophytes: Terrestrial plants which cannot tolerate
extremely dry conditions and pass through long periods without-water.
3.
Mesophytes: Terrestrial plants require moderate quantity of
water.
·
Depending on requirement of
water, animals groped into:
1.
Hydrocoles: Aquatic animals which live in water and require
large quantity of water.
2.
Xerocoles: Terrestrial animals which can tolerate extremely
dry conditions and pass long periods without water.
3.
Mesocoles: Terrestrial animals requiring moderate quantity
of water.
(d)
Rainfall
The rainfall provides water to plants and animals. Rainfall
occurs due to interchange of water between earth’s surface and the atmosphere.
Annual rainfall determines the types of vegetation in any region. Different
regions of the earth receive, different quantity of rainfall depending upon
the geographical features and the availability of moisture laden winds. The
quantity, duration and intensity of rainfall regulate plant life.
(e)
Wind
The wind accelerates transpiration, removes solid moisture
and at high velocities causes soil erosion. Erosion is the removal of the
surface soil, rich in organic matter and fine mineral particles.
(f)
Humidity
Processes as transpiration, absorption of water etc. are
influenced by atmospheric humidity. Humidity, thus, plays an important part in
the life of plants and animals.
(g)
Atmospheric gases
Some principal gases like nitrogen, oxygen, carbon-dioxide,
helium, hydrogen, methane, ozone etc. are found in atmosphere. In addition to
these gases, there are water vapours. Industrial gases, dust, smoke particles,
micro-organisms etc. are present in the atmosphere. These gases have important
influence on the environment.
(h)
Salinity
Levels of salt affects the balance of water organisms through
osmosis. The most aquatic organisms live in habitats of freshwater or salt
because it has limited ability to osmoregulate.
II.
Edaphic Factors
Edaphic
factors deals with different aspects of soil, such as the structure and
composition of soil, its physical and chemical features. Differences in soils
is the main cause of occurrence of change of vegetation and animals. pH and
physical structure also affects the distribution of animals and plants
Soil has mainly the following components:
(i) Mineral matter.
(ii) Soil organic matter or humus.
(iii) Soil water/soil solution.
(iv) Soil Atmosphere.
(v) Biological system (fauna of bacteria, fungi,
algae, protozoa, ratifies, arthropods, etc.).
III.
Topographic Factors
Its concerned with physical geography of the earth are
known as topographic factors. These factors influence vegetation which causes
variation in climate of a geographic region. The different topographic factors
are:
1.
Altitude of the
place
As the altitude above the sea level increases, there happens a decrease
of temperature. Besides, the values of pressure, humidity, wind velocity etc.
also changes. All these factors together give a definite pattern of
vegetational zone.
2.
Steepness and exposure of the slope
The slope of
mountain affects the nature of vegetation. In northern hemisphere, south facing
slopes receives more solar radiation than the north facing slope. the steepness
of slope accelerates the downward movement of surface water. The downward
movement of water over the slope causes soil erosion and as a result, the
vegetation disappears from that area.
3.
Direction of the mountain chains.
Its influences the
rainfall in an area. If the mountain chains lie in the path of wind full of
water vapour, then there is heavy rainfall on the wind striking side on the
mountain chain.
B. BIOTIC
The biotic factors
constitute the living organisms of the environment and definitely they have
their interactions. All types of interactions of living organism called symbiosis.
It can devided into positive interaction and negative interaction.
1.
Positive Interaction
When the
population help one another or both the species benefit.
(a)
Mutualism
Mutually
beneficial inter-specific interactions with permanent and obligatory contact
indispensable for their survival is termed as mutualism. Generally, two species
(population) enter into some contact beneficial to each other. Example: Pollination by Animals (Bees, moths,
butterflies etc. derive their food from plants and bring about pollination), Dispersal
of fruits and seeds (The birds eat the fruits and the seeds contained in fruits
are left through excrement at different places), Symbiotic nitrogen fixers (The
bacterium Rhizobium forms nodules in the roots of leguminous plants and lives
symbiotically with the host. Bacteria derive food from the higher plants and in
return fix gaseous nitrogen which is necessary for the plants.)
(b)
Commensalism
Its represents two
or more populations living together without entering into any kind of
physiological exchange. In this process, one is benefited without any effect on
the other.
2.
Negative Interaction
(a)
Antibiosis.
Through the
production of some substances or environmental conditions due to metabolic
pathways, there is death of one organism by another.
(b)
Parasitism.
A parasite is the
organism living on or in the body of another organism and deriving its food
from its tissues.
(c)
Predation.
Predator is free
living organism which kills and devours individuals of other species.
(d)
Competition.
When two organisms
survive for something which is inadequate leads to competition. Its devided
into:
·
Intra-specific.
Competition
occurs between the members of same population.
·
Inter-specific.
Competition
occurs between the populations of different species
MIND MAP
Refflection
I know that environmental factors in ecology are
divided into two, namely biotic and abiotic component. Abiotic component
consists of objects cannot live while biotic consists of living things. Biotic
factors include, among others, is the light of the Sun, water, wind,
temperature, humidity and soil. Whereas biotic factors consist of interacting
living thing. The interactions that happen to be called positive or negative.
Biotic and abiotic component factors so intertwined with each other for the
balance of the ecosystem.
http://www.environmentalpollution.in/environment/5-ecological-factors-that-constitute-the-environment-of-an-organism/178






Danke.... Mudah dipahami
BalasHapusDitambah lagi rujukan dari buku atau jurnal
goodjob ais kalimat mudah dipahami tapi saran diperhatikan lagi ya font sama kerapiaan setiap paragraf
BalasHapussudah baik Aisyatur. saya suka dengan blognya. tapi saya sarankan untuk memperhatikan tulisannya supaya lebih menarik.
BalasHapusIsinya mudah untuk dipahami karena disajikan dalam bentuk poin dan disertai dengan gambar.
BalasHapuslebih dirapikan lagi yaa tulisannya